Computer aided design (CAD) has revolutionised the way designers work across a wide range of industries. From major engineering projects and architecture to complex electronic circuitry and even the world of fashion, professional designers are utilising CAD programs to realise their visions with a higher degree of accuracy and versatility.
Here are some of the major benefits that CAD software can bring to any business that incorporates design elements into its operations:
Cost and productivity
CAD programs can greatly boost the productivity of your design teams. Designs can be made with great precision, tweaked and edited, with different components or aspects of the overall design all able to be worked on separately or linked to the whole. Complex designs can be rotated or even ‘flown through’ in full 3D while geometries and components can be copied or mirrored, cutting down on repetitive drafting tasks. Prototypes, early designs and incomplete models can be easily and conveniently saved, allowing your designers to try new approaches or additions without having to start from scratch (or, appropriately, going back to the drawing board).
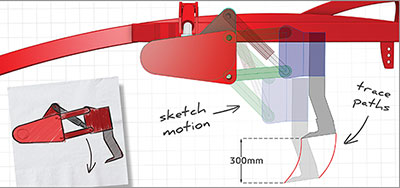 All of this can save a lot of time and therefore money. It can also allow you to try out different designs without adding too much to the overall costs. The savings you make can be substantial when you allow for the cost of the software package and any hardware upgrades required to run it.
All of this can save a lot of time and therefore money. It can also allow you to try out different designs without adding too much to the overall costs. The savings you make can be substantial when you allow for the cost of the software package and any hardware upgrades required to run it.
Communication
Designers rarely work in a bubble. There will usually be consultations and collaborations with other departments, clients and outside agencies. Using CAD can allow you to create clear, easily understandable designs with legible notes. Where two parties are using different software packages, common file types and CAD translation tools will usually allow a design or model created on one system to be viewed within another.
Documentation and data storage
Creating documentation is one of the most important aspects of the design process and CAD programs can be used to document data such as geometries and dimensions of the product, its subassemblies and components. All data created in the design process can be saved to be printed, consulted or used again. This can allow certain components to be used again in another product for example. Tools can also be used to turn data into high-quality technical communications such as: part manuals, assembly instructions and training manuals; which can be useful for both design professionals and other departments within your business.

 Why Your Link Building Efforts Might Fail
Why Your Link Building Efforts Might Fail  How to Request or Give Remote Control in a FaceTime Call on iPhone
How to Request or Give Remote Control in a FaceTime Call on iPhone  The Rise of Intelligent Automation in Business Operations
The Rise of Intelligent Automation in Business Operations  The Best Ideas for Designing Your Custom Printed Ring Binder
The Best Ideas for Designing Your Custom Printed Ring Binder  How Technology is Changing the Way We Play Hearts
How Technology is Changing the Way We Play Hearts  The Rise of Open Source: A Journey to Innovation and Collaboration
The Rise of Open Source: A Journey to Innovation and Collaboration  How SD-WAN Is Revolutionizing Business Networks
How SD-WAN Is Revolutionizing Business Networks  Effective Digital Advertising Strategies for Modern Businesses
Effective Digital Advertising Strategies for Modern Businesses  Tips for Marketing Dental Packages: Easy Ways to Grow Your Reach
Tips for Marketing Dental Packages: Easy Ways to Grow Your Reach 