Flaw in Android’s Mediaserver Component
Details have emerged with regards to another Android weakness which like other latest errors, rotates around how Google backed mobile operating systems tends to handle media files. The vulnerability of the Android Mediaserver could be misused in performing attacks concerning arbitrary code execution. Security researchers at Trend Micro have exposed the flaw in the Android’s Mediaserver component which could be remotely exploited in order to install malware on a target device by sending a specially crafted multimedia message.
Security bug – CVE 2015-3842, tends to affect Android versions 2.3 to 5.1.1 and hence hundreds of thousands of devices are likely to be open to hackers. The danger comes possibly from booby-trapped apps,though nothing serious has occurred so far and there are no known active attacks against this weakness which Google had fixed earlier this month. Applying patches to vulnerable systems could take some time owing to the fragmented nature of the Android ecosystem together with the lack of well organised patch delivery mechanism, in any case on the exterior of Google’s home grown Nexus devices.
Security Error
According to Trend Micro, the latest problem follows a rash of three other main vulnerabilities in Android’s Mediaserver component and the CVE-2015-2823 error develops a resource in trapping phones in endless reboots. Android-21296336 could render the devices silent while CVE-2015-3824 – Stagefright, could be utilised in installing malware through a multimedia message.
On June 19, the security firm revealed the issue together with the corresponding proof of concept – a harmless exploit code which tends to depend on the bug to operate, to the Android Security Team. Google accepted the error as a great severity weakness and published a fix on August 1st.
The security error involves a mediaserver component known as AudioEffect and tends to utilise an unchecked variable which comes from the client generally an app. As per a security researchers from Trend Micro, the vulnerability could be manipulated by malicious app and all that a hacker may require is to convince the user to install an app which may not ask for `any required permission, giving a false sense of security’.
Proof-of-Concept – PoC, Malicious App
Moreover, the researchers have developed a proof-of-concept (PoC), a malicious app which tends to exploit the flaw. This app had been tested on a Nexus 6 handset running android 5.1.1 Build LMY47Z. Once the app has been installed on the device, it crashes the Android’s mediaserver component by overflowing the buffer pReplyData in the heap though if the mediaserver component does not seem to crash, then the PoC app will tend to close and run again.
There has not been any indication of active attacks so far against this vulnerability though researchers are of the opinion that the flaw could be exploited in order to provide complete control on the target device. Though Google has fixed it and taking into consideration the shaky history of device manufacturers as well as carriers rolling out patches, it is unknown how long the companies would be taking to update the vulnerable devices. We could wait and watch for some more upcoming developments.

 Why Your Link Building Efforts Might Fail
Why Your Link Building Efforts Might Fail  How to Request or Give Remote Control in a FaceTime Call on iPhone
How to Request or Give Remote Control in a FaceTime Call on iPhone  The Rise of Intelligent Automation in Business Operations
The Rise of Intelligent Automation in Business Operations  The Best Ideas for Designing Your Custom Printed Ring Binder
The Best Ideas for Designing Your Custom Printed Ring Binder  How Technology is Changing the Way We Play Hearts
How Technology is Changing the Way We Play Hearts  The Rise of Open Source: A Journey to Innovation and Collaboration
The Rise of Open Source: A Journey to Innovation and Collaboration 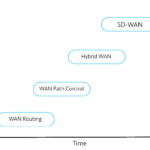 How SD-WAN Is Revolutionizing Business Networks
How SD-WAN Is Revolutionizing Business Networks  Effective Digital Advertising Strategies for Modern Businesses
Effective Digital Advertising Strategies for Modern Businesses  Tips for Marketing Dental Packages: Easy Ways to Grow Your Reach
Tips for Marketing Dental Packages: Easy Ways to Grow Your Reach 